

In May 2018, the Building a Safer Future, Independent Review of Building Regulations and Fire Safety: Final Report, more commonly known as the Hackitt Review, was published and laid out more than 50 recommendations to create a more robust regulatory framework for the building industry as a whole, with particular focus on fire safety.
The government began conducting consultations within the industry to work out how to implement these recommendations effectively. This has led to incremental updates to the Building Regulations through the introduction of new legislation, such as the Fire Safety Act 2021 and the Building Safety Act 2022.
This has significantly changed the regulatory rules and responsibilities for fire safety in a relatively short time. With the release of the latest amendments to Approved Document B on 1st December 2022 and its six-month transition period, which expired on 1st June 2023, it is essential to get up to speed with the current fire regulations and how they apply to commercial roofing.
Whilst this article attempts to make the requirements as clear as possible, if you would like any clarifications or guidance, please get in touch with one of Garland UK’s highly trained Technical Managers.
Building Regulations
The Building Act 1984 is the legislation that forms the framework of all UK building regulations. This is updated directly by parliament and through additional legislation, most recently the Fire Safety Act 2021 and the Building Safety Act 2022. Building Regulations are a set of standards and requirements that must be met when constructing, altering, extending, or converting buildings. These regulations cover a wide range of areas, including energy efficiency, fire safety, structural stability, access for disabled people, and ventilation, among others. They ensure that buildings are safe, healthy, and sustainable for their occupants and the wider environment. Local authorities enforce the regulations, and failure to comply can result in legal action. There are a series of Approved Documents that specify how to comply with the Building Regulations; Approved Document B (ADB) deals with fire safety.
Approved Document B (ADB)
Approved Document B (ADB) explains how to fulfil the requirements for fire safety in the Building Regulations. It is divided into ADB volume 1 (Dwellings) and volume 2 (Buildings other than dwellings). Requirement B3: Internal fire spread (structure), and Requirement B4: External fire spread dictates the requirements that apply to the building envelope, external walls and roofing.
ADB’s last full update was in 2019 to attempt to make the document easier to understand and important to introduce the new Regulation 7(2) of the Building Regulations, which banned combustible materials in or on external walls of the newly defined ‘relevant buildings’. In most cases, combustible materials should also not be used on the newly defined ‘specified attachments’, which include elements attached to the external walls of a building, most notably balconies. The LRWA, NFRC and SPRA, have produced a useful Guidance Document to help clarify and apply these changes. It was additionally amended in 2020, most recently in December 2022.

Relevant Buildings
This is any building that is 18m above ground level and contains one or more dwellings, an institution, or a room for residential purposes. It now also includes student accommodation, care homes, sheltered housing, hospitals, dormitories in boarding schools, hostels and boarding houses.
In fact, for all intents and purposes, no residential building above 11m from ground level can now use any combustible materials in or on external walls.
Some exclusions to the definition of a ‘Relevant Building’ include military barracks, any accommodation provided by the MOD and secure residential institutions. You can see the full details of exclusions here.

Specified Attachments
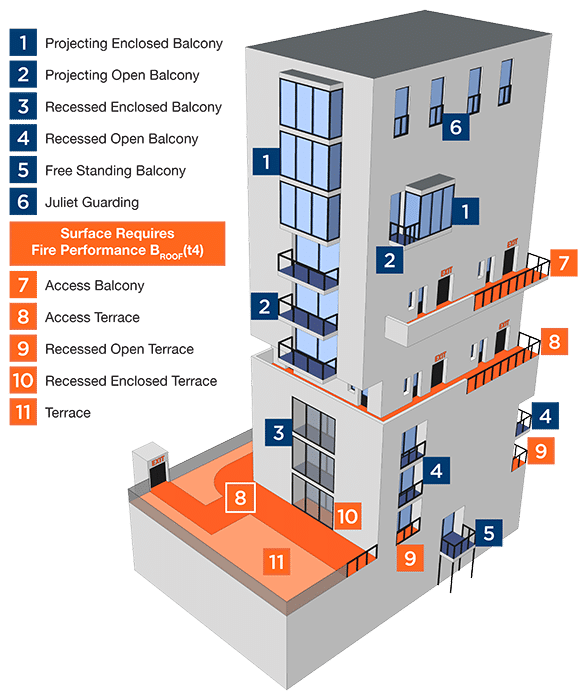
This new term has caused a great deal of confusion; what should be considered a flat roof and what should be considered a balcony? It appears to contradict the European Commission Directive 2000/553/EC and Regulation 7(3) if the definition of a balcony is deemed to include an insulated roof. The flat roofing industry, working with other relevant bodies, has come to a common understanding, which is now also mirrored in BS8579:2020 ‘Guide to the Design of Balconies and Terraces’.
Attached balconies are differentiated from roof terraces in that they are not over habited and conditioned spaces. They are usually bolted to, or cantilevering from, the external wall. Also included are most inset balconies. For the purposes of Approved Document B, balconies are not deemed to be roofs unless they are a designated providing means of escape.
For areas that are correctly deemed to be balconies, i.e. ‘specified attachments’ on ‘relevant buildings’, non-combustible material must be used. However there is an exception made by Regulation 7(3) that excludes the waterproofing membrane from this requirement.
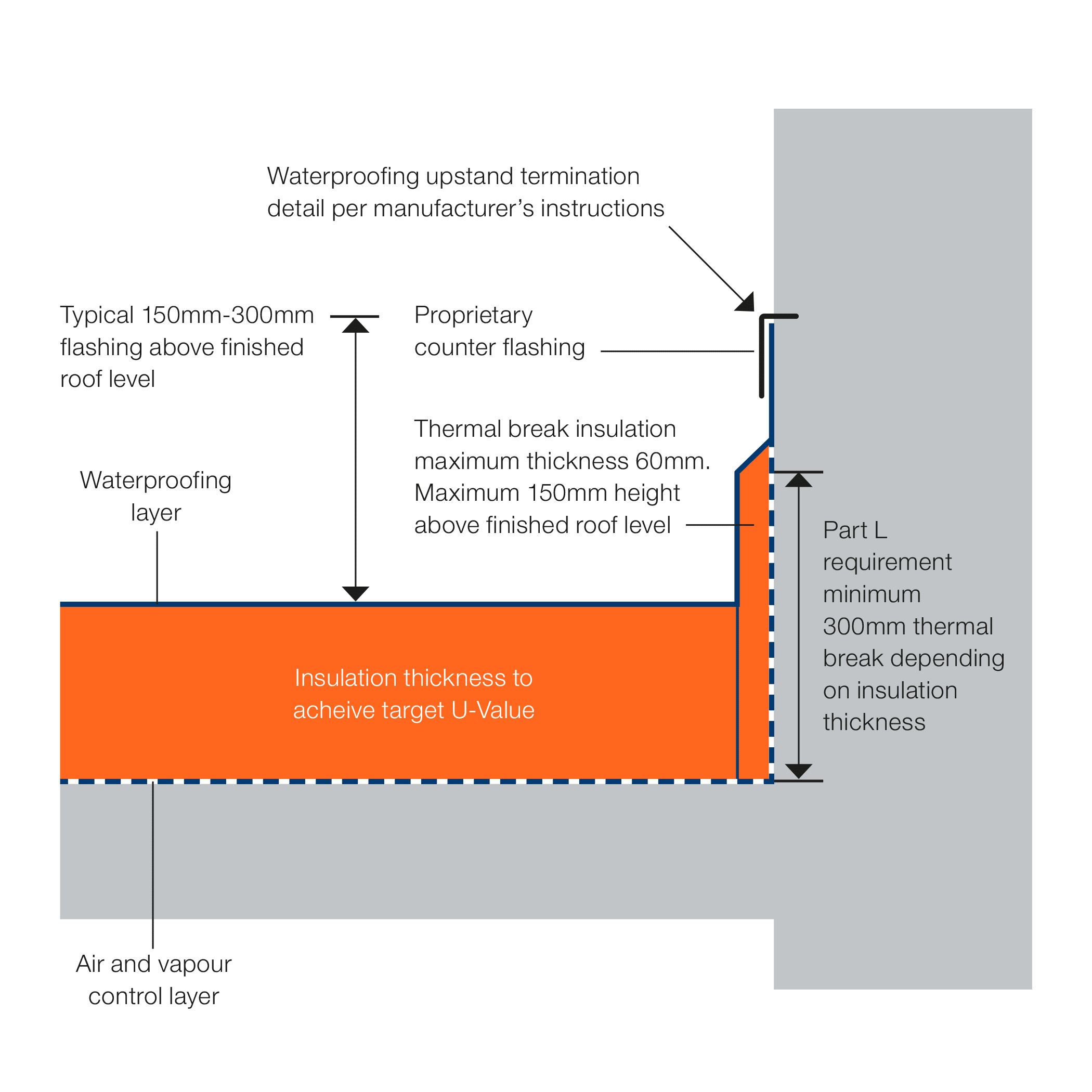
Termination of Roofing Materials on ‘Relevant Buildings’
The exception to the use of non-combustible membrane in Regulation 7(3) has caused another serious area of confusion, how do you safely terminate a roof or balcony where it abuts a wall. Again the LRWA, NFRC and SPRA Guidance Document has resolved this issue.
Insulation used as a thermal break on the face of a wall or abutment is exempt from the non-combustible ban, provided it is no thicker than 60mm and does not go higher than 150mm above the finished roof level or walking surface. If for any reason the thermal break goes higher than this, or if it crosses an internal fire compartment line, then non-combustible insulation must be used.
Requirement B3: Internal fire spread (structure)
Fire compartmentation is used internally to stop the spread of fire throughout a building. This basically entails separating the building into compartments using fire-resistant walls, floors, and doors, so that the fire is contained within a single compartment in the event of a fire.
Where a fire compartment wall forms a junction with the structure of a roof, the roof covering must be classified to BROOF(t4) and extend 1500mm either side of the wall. The roofing substrate or deck must be classed A2-s3 d2 or better.. In buildings under 15m high from ground level and purpose groups 1,2,3 or 5 other than 2(a), a substrate of B-s3 d2 or worse can be used. In all cases, fire-stopping is to be carried up to the underside of the roof covering.

Requirement B4: External fire spread
B4 sets out the requirements to prevent the external spread of fire for external walls and roofs. It states that:
- The external walls of the building shall adequately resist the spread of fire over the walls and from one building to another, having regard to the building’s height, use and position.
- The roof of the building shall adequately resist the spread of fire over the roof and from one building to another, having regard to the use and position of the building.
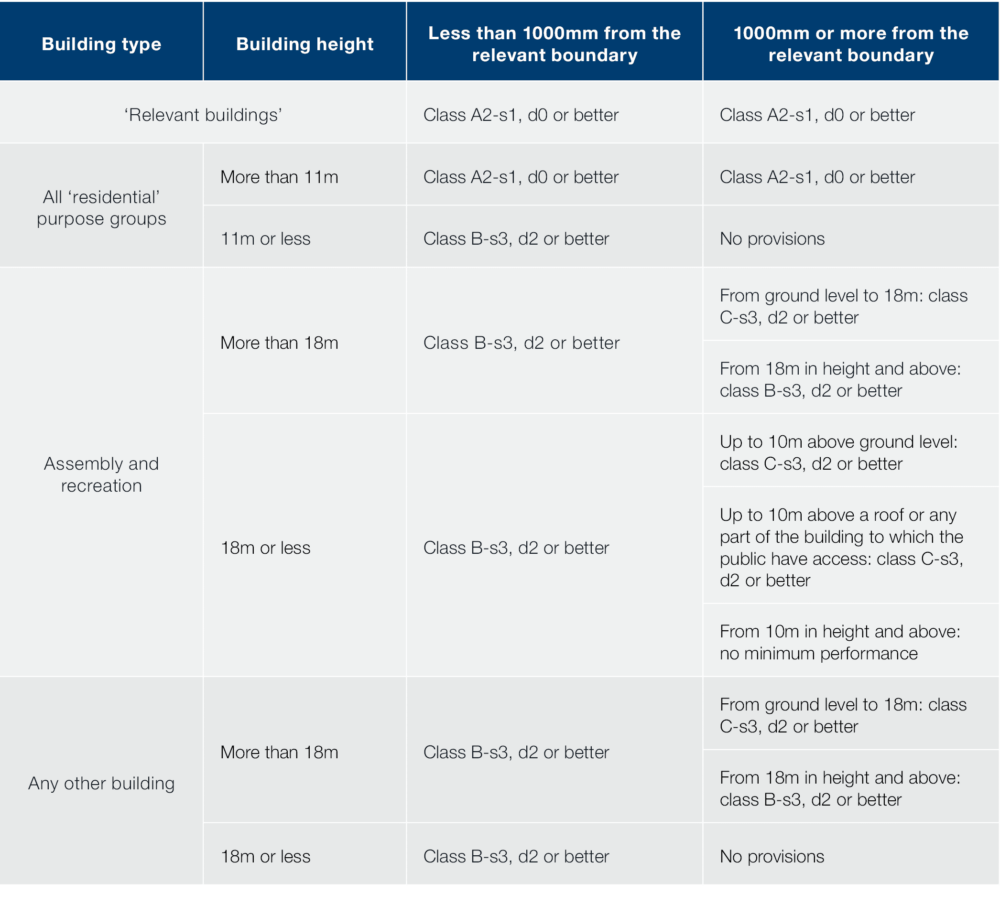
The outermost material used for external walls must meet the combustibility requirements in table 10.1. The distance to the boundary of the property, its height and use dictate what materials can be used.
Below is a simplified version of the table:
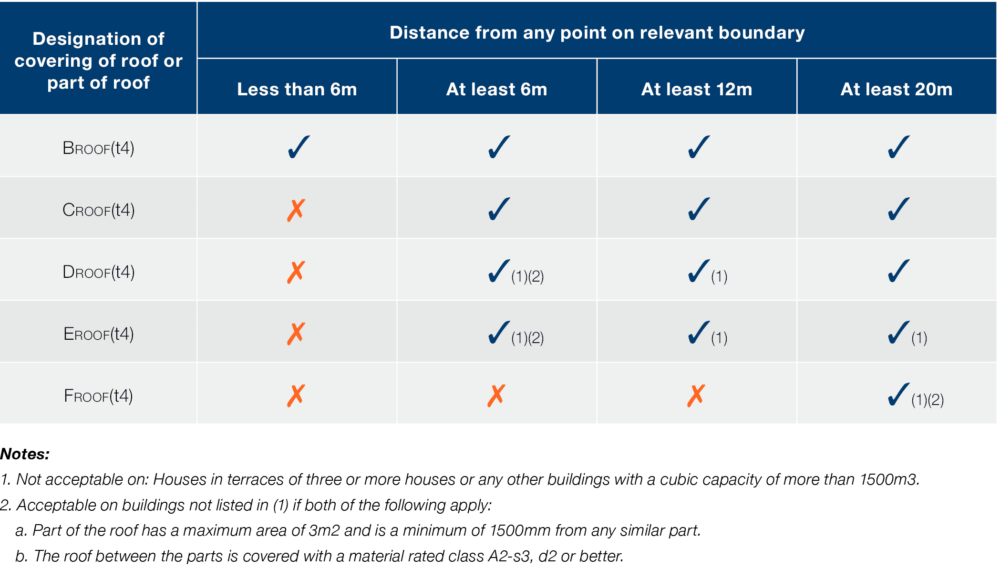
For roofs, Requirement B4 sets out in Table 12.1 the required classification that the roof covering must achieve. This is determined by the distance to the boundary of the property. Only the highest classification BROOF(t4), can be used unrestricted on any building, which is why Garland UK only provides roofing solutions that achieve this standard.
When a Roof Becomes a Wall
It is fundamental to understand when a roof becomes a wall, as different testing standards and classifications will be applicable when ensuring compliance with Approved Document Part B.
At the point a roof is 70 degrees in pitch or greater, this part of the construction will be classified as a wall. Therefore, within Approved Document Part B, requirement B4, guidance should be followed for the reaction to fire performance of external surface of walls.
This detail can often be observed at mansards when the mansard makes up part of the roofing system. However, when the mansard is over 70 degrees in pitch, different regulations relating to fire performance are applicable as this is now classified as a wall. More notably, although combustible insulation types are allow within roofing systems on buildings over 18m in height under the BROOF(t4) classification, combustible materials are not permitted within external walls as described in regulation 7(4), materials must be of class B-s3, d0 or better.
Fire Testing Classifications
If you’ve been wondering what all these different fire classifications actually mean, don’t worry; this section should hopefully clarify things.
CEN/TS 1187:2012 – Test methods for external fire exposure to roofs
Dictates four test methods used to determine a roof’s resistance to external fire exposure. Tests methods 1-3 are widely used across Europe, with only the UK using method 4, which incorporates 2-stage testing and is more rigorous.
BS EN 13501-5 – Fire classification of construction products and building elements. Classification using data from external fire exposure to roof tests.
Sets out the required performance that the roofing system must attain to get its classification, with Broof(t4) being the best and Froof(t4) being the worst performance, as shown below.
All Garland UK roofing systems achieve the highest Broof(t4) classification and can be used unrestricted on any building.

EN 13501-1: Fire classification of construction products and building elements
This classification shows how a product performs to three different criteria, firstly, how it contributes to the spread of fire; secondly, how much smoke it produces; and finally, if it produces flaming droplets and particles.
The tables below show various ratings that make up the total classification:

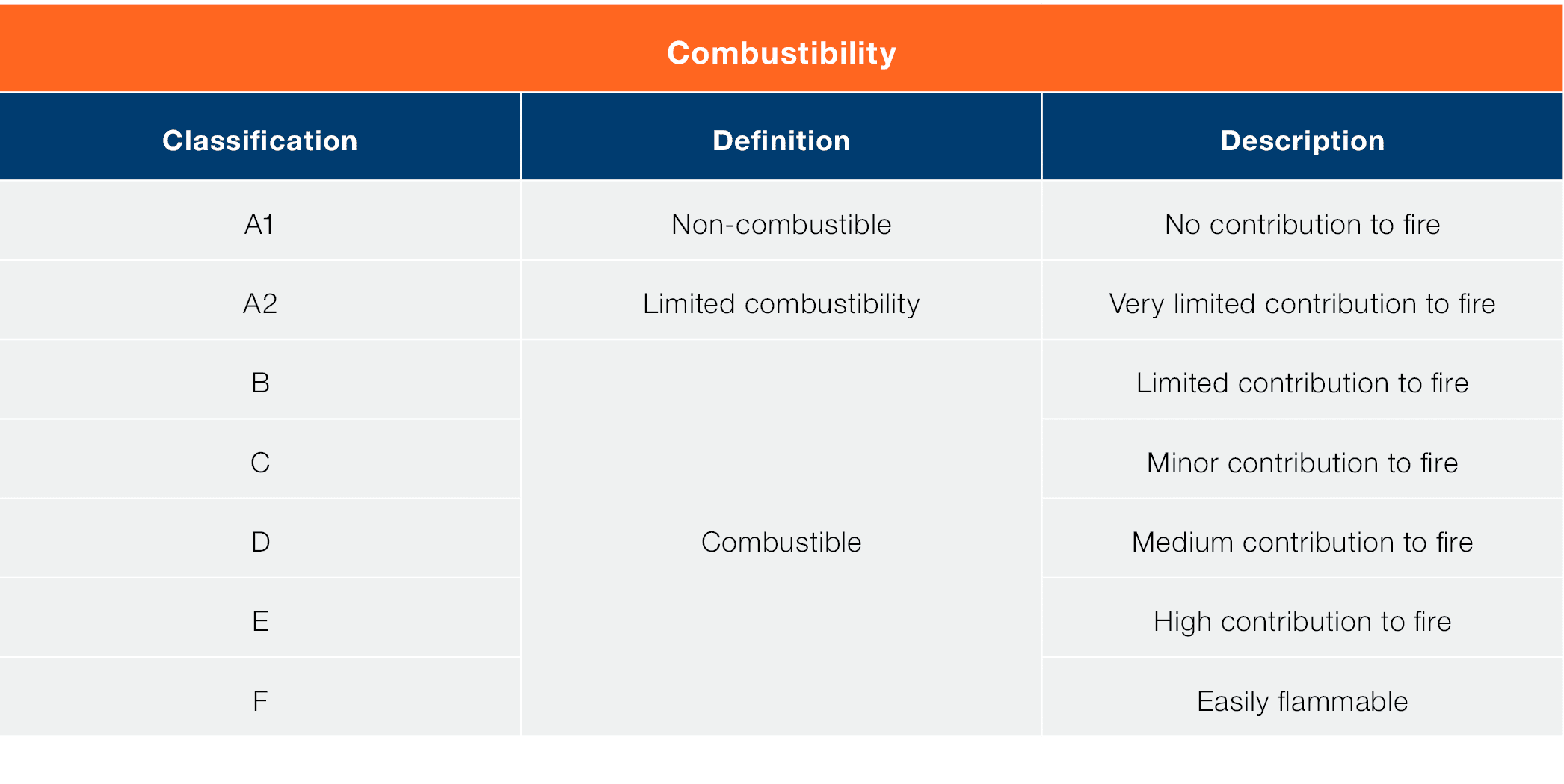

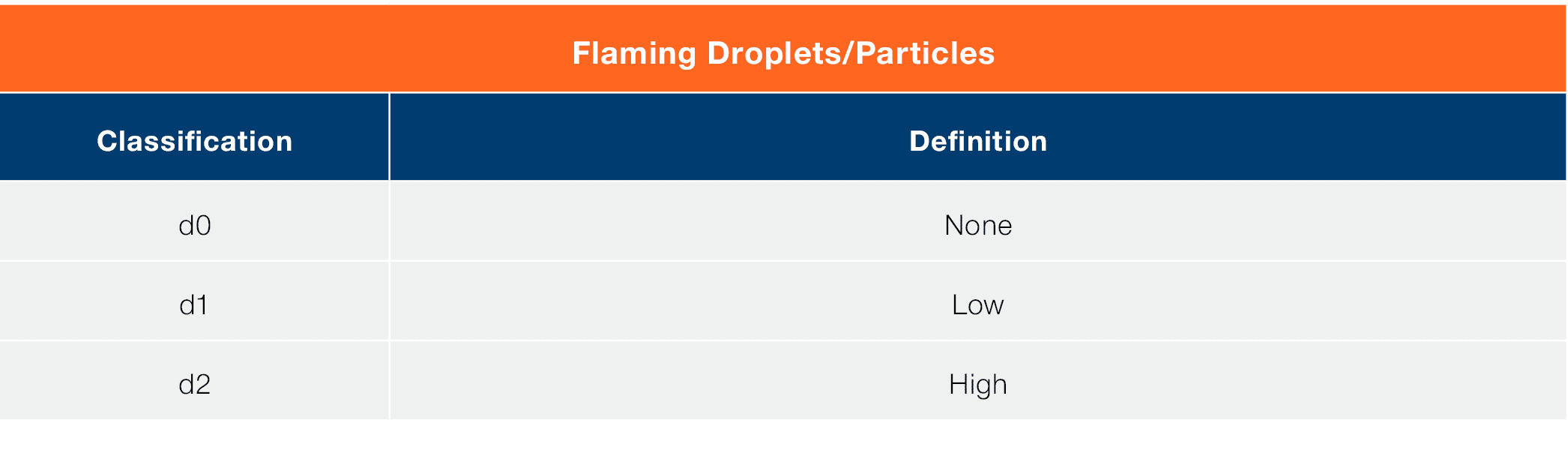
So, a product with a classification A1-s1 d0 would be non-combustible, produce little to no smoke and not cause any flaming droplets or particles.
Responsibilities of Fire Safety Order for Building Owners or Managers
The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 (also known as the Fire Safety Order) is a UK law that sets out the fire safety responsibilities of building owners and managers and the steps they must take to reduce the risk of fire and protect people in the event of a fire.
The Fire Safety Order applies to most non-domestic buildings in England and Wales, including:
- Workplaces, such as offices, factories, and warehouses
- Public buildings, such as schools, hospitals, cinemas, and museums
- Residential buildings, such as flats, hotels, hostels, boarding houses
- Assembly and leisure buildings, such as places of worship, community halls, and sports stadiums
- Shops and retail premises
- Mixed-use buildings
Single-family homes are not covered, although it does apply to multi-occupancy houses in multiple occupations (HMOs). The Fire Safety Order places responsibility for fire safety in buildings on the “responsible person”. Depending on the circumstances, this can be the building’s owner, manager, or occupier.
The responsible person is responsible for:
- Ensuring that the premises reach the required standards.
- Providing employees or occupants with adequate fire safety training, which would include:
- Induction training to cover general fire awareness.
- Periodic refresher training or extra training where the level of fire risk increases as a result of changes in your operations.
- Training to support people in meeting their fire safety duties – for example, keeping your ‘responsible people’ up to date.
- Training to build appropriate skills such as fire risk assessment, fire warden or using fire extinguishers.
- Conducting a regular fire risk assessment to:
- Identify the fire hazards.
- Identify people at risk.
- Evaluate, remove or reduce the risks.
- Record your findings, prepare an emergency plan and provide training.
- Review and update the fire risk assessment regularly.
It’s important to note that these are general responsibilities, and the specific requirements can vary depending on the type and use of the building. More information is available from the government’s Fire Safety in the Workplace site, or, as always, Garland UK are here to help; please contact one of our Technical Managers if you would like further advice or to arrange a complimentary roof assessment.
How can Roofing be Upgraded to meet the Safety Standard?
If, during the course of conducting a fire risk assessment, you discover that your roof is not up to standard, there are a number of potential solutions available to you. Garland UK’s range of Cold Applied Liquid Roofing Systems can be applied to most roofing surfaces without the need for a full roof replacement. It can be installed quickly and will immediately reclass your roof to a BROOF(t4) standard. Our R-MER CLAD could also be used to overclad the existing roofing structure, which would again reclass the roof to BROOF(t4).
If there are issues relating to the fire compartmentation where it joins the roof, then internal works would need to occur. If budgets allow, the existing roofing structure can be removed and replaced with one of our Metal or Green Roofing systems.
Practical Advice to Make Your Building Safe
Here are some practical steps building owners and managers can take to help ensure the safety of your building and its occupants:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment: Start by conducting a thorough assessment of the building and building envelope to identify any potential fire and safety hazards, including the condition of fire-resistant elements, roof membranes, and roof components.
- Upgrade fire-resistant elements: Upgrade fire-resistant elements such as walls, floors, and ceilings to ensure they meet the latest fire-resistance standards.
- Maintain fire safety systems: Regularly maintain and test fire safety systems, including fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and emergency lighting, to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Educate occupants: Occupants should be familiar with the building’s fire safety procedures, including evacuation routes and the use of fire alarms and sprinkler systems.
- Regular maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the building envelope and roof to ensure it is in good condition and identify and address any potential hazards.
Fire regulations are now more robust than ever, it is essential to carry out a thorough fire risk assessment of your building to ensure that there is no risk to residents or the building itself.
Sam Rigden, Technical Manager, Garland UK
